Imagio® delivers diagnostic confidence at the point of care
With new technology that has never been available before, Imagio® provides substantially improved confidence in breast cancer diagnostics using a non-invasive, real-time OA/US scan, supported by our proprietary AI-driven SenoGram® decision support. The simplified and streamlined care pathway offers the first FDA-approved device to effectively reduce the delays, discomfort, and costs of diagnosing breast cancer.
Radiologists Patient Experience Practice Efficiency Read our eBook
Laser light in. Sound out.
The new imaging modality to diagnose breast cancer in real-time
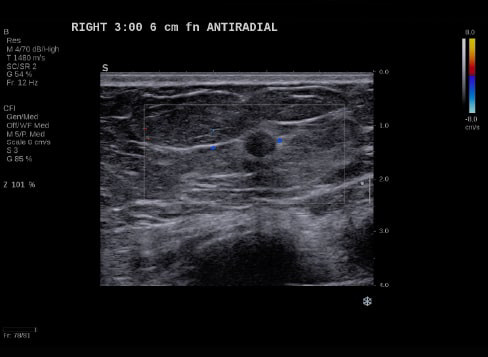
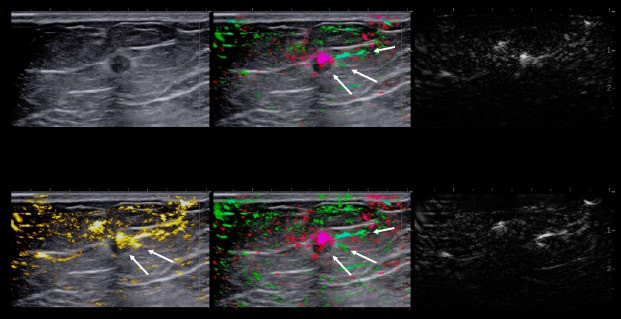
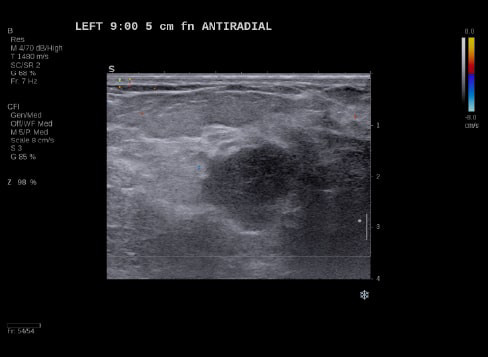
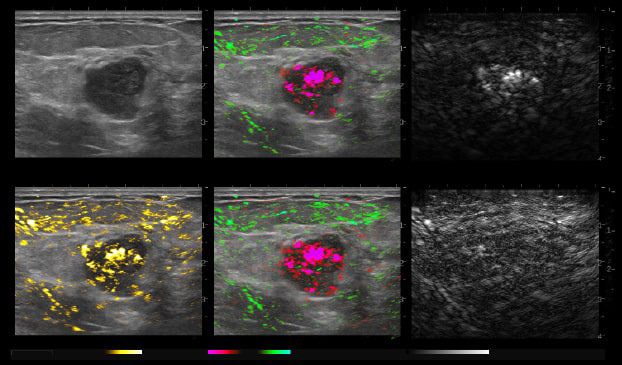
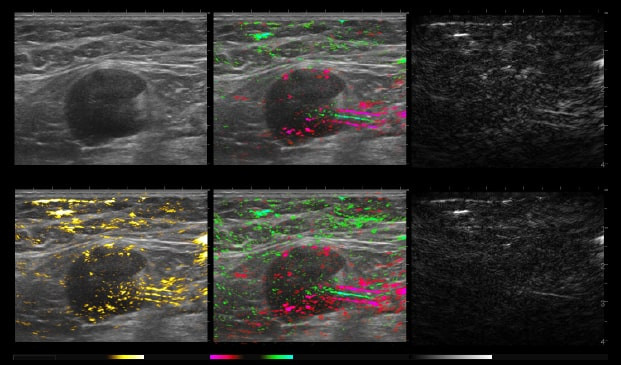
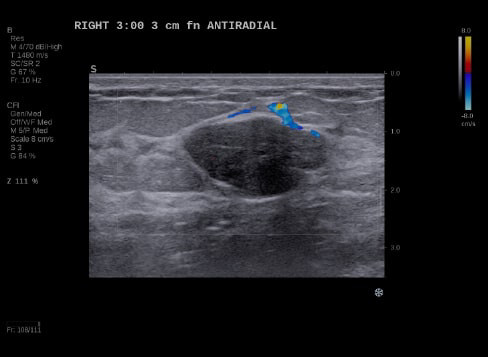
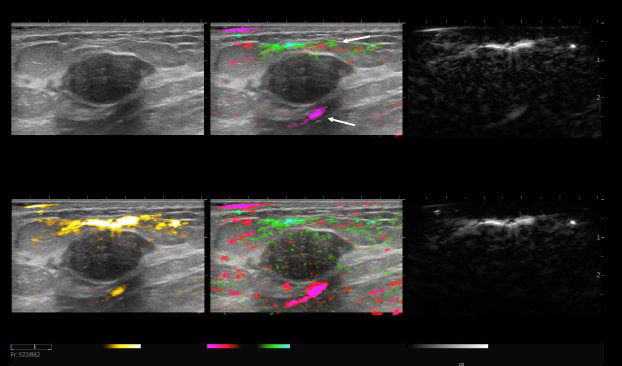
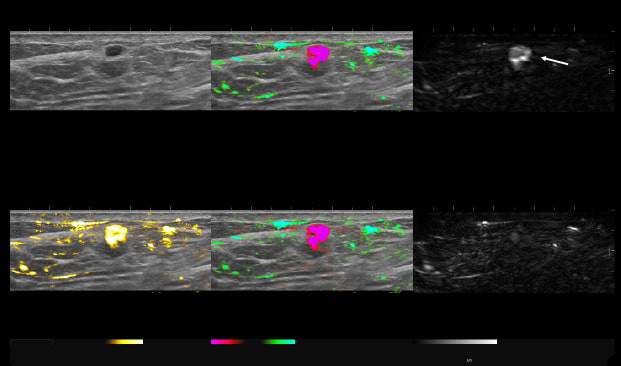
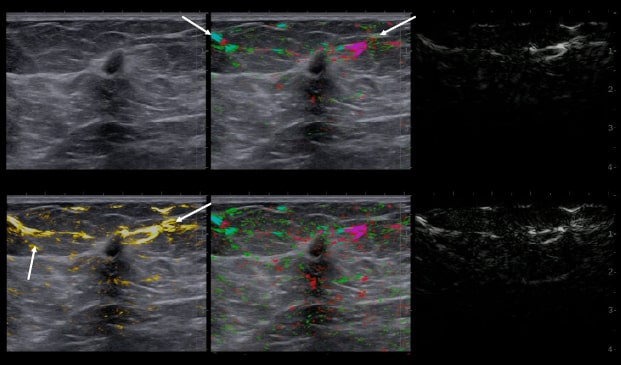
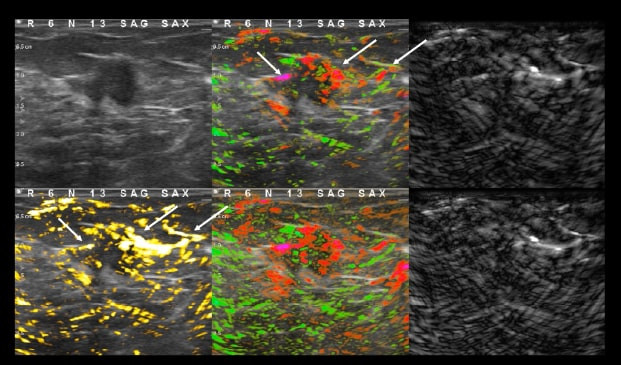
By transmitting laser light through suspicious breast tissue, Imagio® returns ultrasound signals that can display both functional and anatomical information about the relative blood and oxygen concentration. This enables clinicians to differentiate malignant and benign tissue: in a full-color display.
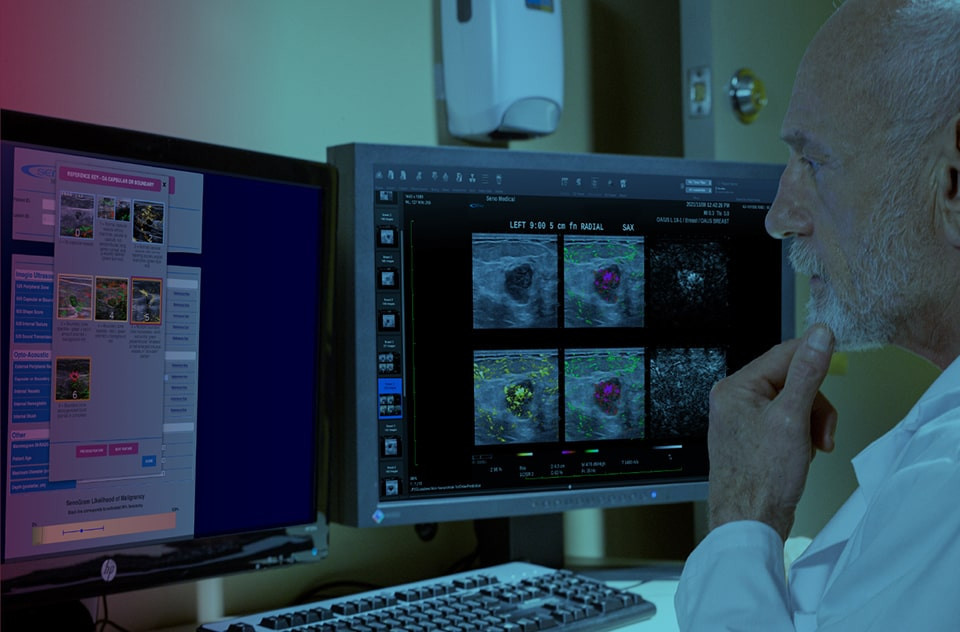

AI-based decision support
Accurately assign diagnostic BI-RADS
Proven to make clinicians more accurate, our proprietary SenoGram® provides AI-driven decision support in assessing likelihood of malignancy (LOM).
View SenoGram® brochure Interact with SenoGram®
A simple transition that improves practice efficiency and profitability
Imagio® integrates into your existing diagnostic workflow over time, similar to how tomosynthesis was introduced. The technology can be easily adopted with the support of SenoGram® and training from a leading Breast Ultrasound expert, Dr. Tom Stavros through Seno University.
Request demo See ROI example
Our nationwide roadshow can bring Imagio® to your facility or you can start the conversation with a Seno rep today to get more details.
References
- Panigrahi B, Editorial Comment: The Value of Decision Support in Breast Ultrasound. AJR 2022 Dec 21
- Seiler SJ, Neuschler EI, Butler RS, Lavin PT, Dogan BE. Optoacoustic imaging with decision support for differentiation of benign and malignant breast masses: A 15-reader retrospective study. AJR Am J Roentgenol. December 7, 2022.